栈和队列的应用
2022.09.12
栈在括号匹配中的应用
x
typedef struct{ char data[MaxSize]; int top;}SqStack;
// 初始化void InitStack(SqStack &S){ S.top=-1;}
// 判断栈是否为空bool EmptyStack(SqStack S){ return S.top==-1;}
// 入栈bool Push(SqStack &S, char x){ return S.top==MaxSize-1 ? false : S.data[++S.top]=x;}
// 出栈bool Pop(SqStack &S,char &x){ return S.top==-1 ? false : x=S.data[S.top--];}
/*考试时这样写#define MaxSize 20typedef struct{ char data[MaxSize]; int top;}SqStack;
// 初始化栈void InitStack(SqStack &S)
// 判断栈是否为空bool EmptyStack(SqStack S)
// 入栈bool Push(SqStack &S,char x)
// 出栈bool Pop(SqStack &S,charchar &x)
*/
bool BracketCheck(char str[]){ SqStack S; InitStack(S); char x; for(int i=0;i<strlen(str);i++){ printf("%c",str[i]); if(str[i]=='('||str[i]=='['||str[i]=='{') Push(S,str[i]); if(str[i]==')'||str[i]==']'||str[i]=='}'){ if(EmptyStack(S)) return false; Pop(S,x); if(str[i]==')' && x!='(') return false; if(str[i]==']' && x!='[') return false; if(str[i]=='}' && x!='{') return false; } } return EmptyStack(S);}
int main(){ char *a; strcpy(a,"{}[]"); printf("\n判断匹配: %d\n",BracketCheck(a)); return 0;}栈在表达式求值中的应用
精要总结:
- 中缀转前缀表达式,左优先
- 中缀转后缀表达式,右优先
- 后缀计算:1 2 +,看到运算符,弹出两个数计算;看到数字,压入栈中
- 前缀计算:+ 1 2,看到第二个数字,弹出运算符;看到运算符,压入栈中
下面是中缀转后缀的C语言实现
int GetPriority(char c){ switch (c) { case '(': return 0; case '+': return 1; case '-': return 1; case '*': return 2; case '/': return 2; case ')': return 3; } printf("Wrong!\n"); return -1;}
char* ToInversePoland(char c0[]){ /* 1. 遇到操作数 ->加入后缀表达式 2. 遇到‘(’入栈, 遇到‘)’依次弹出站内运算符加入后缀表达式直到‘(’. (注意, 括号不入后缀表达式) 3. 遇到运算符. 依次弹出运算及高于或等于当前运算符的所有运算符, 直到括号或栈空为止. 然后把当前运算符入栈. 4. 处理完所有字符后, 把栈中运算符依次弹出. */ char c[64] = "("; strcat(c,c0); strcat(c,")"); static char InversePo[64] = ""; // 后缀表达式 int index = 0; LinkStack stack; LinkStackInit(stack); Element e; for(int i=0; i<strlen(c);i++){ if('0'<=c[i]&&c[i]<='9'){ InversePo[index++] = c[i]; }else if(c[i]=='('){ LinkStackEn(stack, ele_build((int)c[i])); }else if(c[i]==')'){ while(LinkStackDe(stack,e)){ if(ele_get_weight(e)!='(') InversePo[index++] = (char)ele_get_weight(e); else break; } }else if(c[i]=='+'||c[i]=='-'||c[i]=='*'||c[i]=='/'){ while(LinkStackGet(stack,e)){ if(GetPriority((char)ele_get_weight(e))< GetPriority(c[i]))break; LinkStackDe(stack,e); if((char)ele_get_weight(e) != '(') InversePo[index++] = (char)ele_get_weight(e); } LinkStackEn(stack, ele_build((int)c[i])); }else{ return NULL; } } InversePo[index]='\0'; return InversePo;}
int main(){ char s1[] = "1+(1+2)/3+(2-1)\0"; printf("中缀转后缀 %s = %s\n",s1,ToInversePoland(s1)); // 中缀转后缀 1+(1+2)/3+(2-1) = 112+3/+21-+}
栈在递归中的应用
略
栈在层次遍历中的应用
略
例题
栈的应用不包括( )。 A. 递归 B. 进制转换 C. 迷宫求解 D. 缓冲区
【答案】:D
表达式a*(b+c)-d的后缀表达式是( )。 A. abcd*+- B. abc+*d- C. abc*td- D. -+*abcd
【答案】:abc+*d-,B
下面( )用到了队列. A.括号匹配 B.迷宫求解 C.页面替换算法 D.递归
【答案】:C
利用栈求表达式的值时,设立运算数栈 OPEN。假设 OPEN 只有两个存储单元,则在下列表达式中,不会发生溢出的是( )。 A. A-B*(C-D) B. (A-B)*C-D C. (A-B*C)-D D. (A-B)*(C-D)
【答案】:
A:[AB] [-*(],溢出
B:[{A-BC*-D-}] [] -> B
执行完下列语句段后,i 的值为( )。
x
int f(int x) (return ((x>0) ? x*f(x-1) : 2);}int i;i=f(f(1));A. 2 B. 4 C. 8 D. 无限递归
【答案】:B
对于一个问题的递归算法求解和其相对应的非递归算法求解,( )。 A. 递归算法通常效率高一些 B. 非递归算法通常效率高一些 C. 两者相同 D. 无法比较
【答案】:B
执行函数时,其局部变量一般来用( )进行存储。 A. 树形结构 B.静态链表 C.栈结构 D.队列结构
【答案】:C
执行( )操作时,需要使用队列作为辅助存储空间。 A. 查找散列(哈希)表 B. 广度优先搜索图 C. 前序(根)遍历二叉树 D. 深度优先搜索图
【答案】:B
下列说法中,正确的是( )。 A. 消除递归不一定需要使用栈 B. 对同一输入序列进行两组不同的合法入栈和出栈组合操作,所得的输出序列也一定相同 C. 通常使用队列来处理函数或过程调用 D.栈和队列都是受限的线性表。只允许在表的两边进行运算
【答案】:A
【2009 统考真题】为解決计算机主机与打印机速度不匹配的问题:通常路置一个打印数据缓冲区,主机将要输出的数据依次写入该缓沖区,而打印积则依天从该缓沖区中取出数据。该缓冲区的逻辑结构应该是( )。 A. 栈 B. 队列 C. 树 D. 图
【答案】:B
【2012 统考真题】已知操作符包括
+,-,*,/,(,)。将中级表达式a+b-a*((c+d)/e-f)+g转换为等价的后级表达式ab+acd+e/f-*-g+时,用栈来存放暂时还不能确定运算次序的操作符。栈初始时为空时,转换过程中同时保存在栈中的操作符的最大个数是( )。 A. 5 B. 7 C. 8 D. 11【答案】:
+g,max: 5[]
ab+acd+e/f-*-g+
A
【2014 统考真题】假设栈初始为空,将中缀表达式
a/b+(c*d-e*f)/g转换为等价的后缀表达式的过程中,当扫描到f时,栈中的元素依次是( )。 A. +(*- B. +(-* C. /+(*-* D. /+-*【答案】:
f)/g,B[+(-*]
ab/cd*e
【2015统考真题】己知程序如下:
x
int S(int n)return (n<=0) ? 0 : s(n-1)+n;void main()cout<< S(1);程序运行时使用栈来保存调用过程的信息,自栈底到栈顶保存的信息依次对应的是()。 A. main()-s(1)-s(0) B. S(0) -S(1) -main() C. main()-s(0)-S(1) D. S(1) -S (0) -main ()
【答案】:[main() - S(1) - S(0)],A
假设一个算术表达式中包含圆括号、方括号和花括号3种类型的括号,编写一个算法来判别表达式中的括号是否配对,以字符"\0" 作为算术表达式的结束符.
bool valid(char c[]){Stack S;for(int i;i<strlen(c);i++){if(c[i]=='('||c[i]=='['||c[i]=='{')Push(S,c[i]);else if(c[i]==')')if(Pop(S)!='(') return false;else if(c[i]==']')if(Pop(S)!='[') return false;else if(c[i]=='}')if(Pop(S)!='{') return false;}return IsEmpty(S);}按下图所示铁道进行车厢调度(注意,两侧铁道均为单向行驶道,火车调度站有一个用于调度的“栈道”),火车调度站的入口处有n节硬座和软座车厢(分别用H和S 表示)等待调度,试编写算法,输出对这n节车厢进行调度的操作(即入栈或出栈操作)序列,以使所有的软座车厢都被调整到硬座车厢之前。
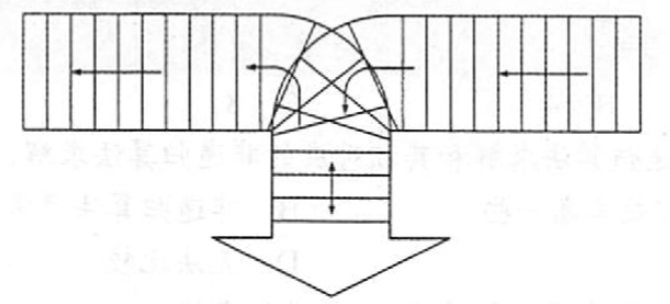
void Transform(LinkList &L, LNode *S, LNode *H,int n){Stack T;for(int i; i<n; i++)if(IsH(GetItemByIndex(L,i)))Push(T,PopItemByIndex(L,i);while(!IsEmpty(T))AddItemAtLast(L,Pop(T));}利用一个栈实现以下递归函数的非递归计算:
Pn = 1, n=0 Pn = 2x, n=1 Pn = 2xP_{n-1}(x) - 2(n-1)P_{n-2}(x), n>1
int f(n,x){if(n==0) return 1;if(n==1) return 2*x;return 2*f(n-1,x) - 2*(n-1)f(n-2,x);}typedef struct {int index;int value;} Element;int f(n,x){Stack S;Element e;int index;int ans1=1;int ans2=2*x;for(int i=n;i>2;i--){Push(S,{i:index++});}while(!IsEmpty(S)){e = Pop(S);e.value = 2*x*ans2 -(e.index - 1)*ans1;ans1 = ans2;ans2 = e.value;}if(n==0) return ans1;return ans2;}